Gluten may seem harmless, but for some individuals, it can silently trigger significant health issues. Many people suffer from gluten sensitivity without realizing it, often misattributing symptoms to other conditions. If left unchecked, gluten intolerance can lead to chronic health problems, affecting everything from digestion to skin health and neurological function.
Understanding the warning signs your body gives you can help protect your well-being. If you suspect gluten might be causing problems, pay attention to these 12 key symptoms that could indicate gluten sensitivity.
1. Hair Loss (Alopecia and Thinning Hair)
Gluten intolerance, especially in individuals with celiac disease, can lead to hair thinning and even bald patches. This happens because gluten can trigger an autoimmune response that attacks hair follicles, leading to conditions such as alopecia areata.
Additionally, gluten-induced intestinal damage may cause nutrient malabsorption, depriving your body of essential vitamins like biotin, iron, and zinc, which are necessary for strong, healthy hair growth. If you experience unexplained hair loss, gluten sensitivity could be a hidden culprit.
2. Digestive Issues (Bloating, Gas, and Stomach Pain)
One of the most common signs of gluten sensitivity is digestive discomfort, which can include bloating, excessive gas, abdominal pain, cramping, diarrhea, constipation, and nausea after eating gluten-containing foods.
These symptoms are frequently misdiagnosed as Irritable Bowel Syndrome (IBS), leading many individuals to suffer unnecessarily. Studies estimate that 10-15% of the global population has IBS, but for some, gluten may be the actual cause.
3. Unexplained Weight Changes (Gain or Loss)
Gluten sensitivity can disrupt metabolism, causing unexpected weight gain or weight loss. This happens because inflammation from gluten affects digestion and absorption, nutrient deficiencies can cause muscle loss and fatigue, and increased bloating can create the illusion of weight gain.
If you’re losing weight unintentionally or struggling with unexplained weight gain, it might be time to evaluate your gluten intake.
4. Hormonal Imbalances (Irregular Cycles & PMS)
Gluten intolerance can throw your hormones off balance, leading to irregular menstrual cycles, severe PMS (Premenstrual Syndrome), unexplained mood swings, and hormone-related acne or breakouts.
These imbalances often become more noticeable during puberty, pregnancy, and menopause, suggesting that gluten may have a significant impact on reproductive health, especially in women.
5. Brain Fog, Anxiety, and Depression
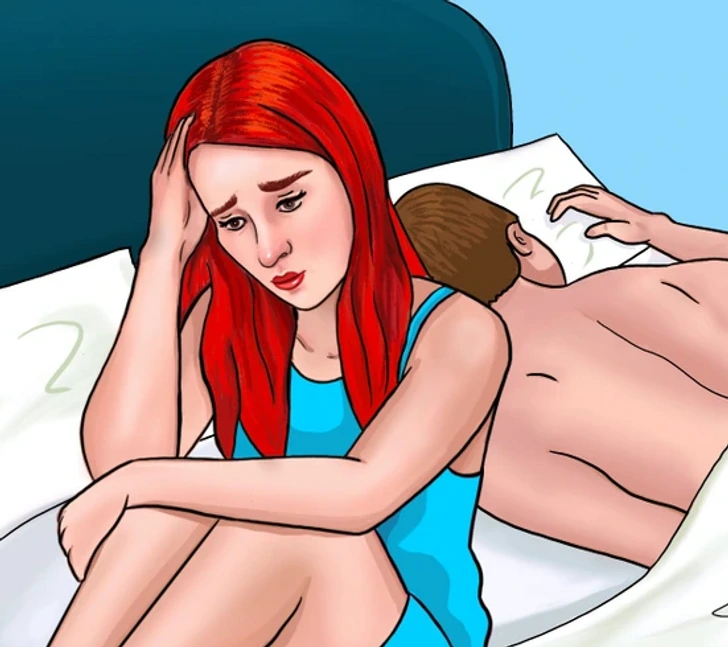

Gluten is closely linked to brain health, and sensitivity can lead to neurological symptoms such as brain fog, difficulty concentrating, memory problems, depression, anxiety, chronic fatigue, and irritability.
Some people with gluten intolerance experience migraines shortly after consuming gluten. If you find yourself struggling with mental clarity, gluten could be affecting your brain function.
6. Skin Problems (Rashes, Psoriasis, and Eczema)
Gluten sensitivity doesn’t just affect your gut—it can also manifest through skin conditions, including psoriasis, eczema, chronic acne, inflammation, and dermatitis herpetiformis (DH), a painful, blistering rash directly linked to gluten.
If your skin issues persist despite using skincare treatments, eliminating gluten could help clear your skin from the inside out.
7. ADHD and Hyperactivity
Studies suggest that a gluten-free diet may improve symptoms of ADHD (Attention-Deficit/Hyperactivity Disorder). Some researchers believe that untreated celiac disease or gluten sensitivity may contribute to cognitive and behavioral disorders.
Parents of children with ADHD often report improved focus and calmer behavior after removing gluten from their diets.
8. Weak Teeth and Frequent Cavities
Gluten intolerance can affect nutrient absorption, leading to weakened enamel, tooth sensitivity, frequent cavities despite good oral hygiene, and chronic mouth ulcers.
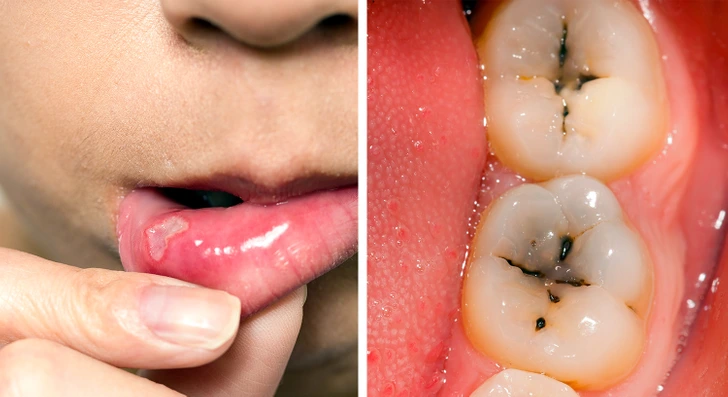
If you have persistent dental problems, it could be due to gluten-related calcium and vitamin D deficiencies.
9. Iron-Deficiency Anemia
Many people with celiac disease struggle with iron-deficiency anemia because their bodies fail to absorb iron properly. Symptoms include fatigue, dizziness, pale skin, brittle nails, and shortness of breath.
If you’re constantly exhausted despite getting enough rest, low iron levels caused by gluten intolerance might be to blame.
10. Increased Risk of Autoimmune Diseases
Many individuals with autoimmune disorders have a history of gluten intolerance. Conditions linked to gluten-induced immune responses include Hashimoto’s Thyroiditis (autoimmune thyroid disease), Rheumatoid Arthritis, Multiple Sclerosis (MS), Type 1 Diabetes, Lupus, and Crohn’s Disease.
Since gluten triggers chronic inflammation, it can worsen autoimmune symptoms and increase the risk of developing new conditions.
11. Tonsil Stones and Persistent Sore Throat
Though rarely discussed, some people with gluten sensitivity report frequent tonsil stones, which are hard, white deposits that form in the tonsils. This happens because gluten can cause chronic inflammation, leading to recurrent sore throats, swollen lymph nodes, bad breath, and difficulty swallowing.
Surprisingly, many patients notice tonsil stones disappearing after switching to a gluten-free diet.
12. Gluten-Induced Hair Loss
In addition to alopecia, gluten intolerance can cause thinning hair due to malabsorption of vital nutrients like iron, zinc, and biotin. Since hair follicles rely on these nutrients for growth, a deficiency can lead to weaker, more brittle hair strands.
The good news is that many people experience significant hair regrowth after adopting a gluten-free diet.
How to Treat Gluten Sensitivity

If you suspect gluten intolerance, follow these steps:
Get Tested: A blood test can check for celiac-related antibodies, but gluten must be present in your diet before testing for accurate results.
Eliminate Gluten: Remove wheat, barley, rye, and processed gluten-containing foods from your diet.
Eat Whole, Naturally Gluten-Free Foods: Focus on fresh fruits and vegetables, lean proteins, and gluten-free grains like quinoa and rice.
Monitor Symptoms: Track changes in energy levels, digestion, skin, and mood.
Final Thoughts: Listen to Your Body
Gluten intolerance can manifest in many ways, affecting digestion, skin, hormones, mental clarity, and more. If you suspect gluten sensitivity, pay close attention to your symptoms and consider eliminating gluten to see if your health improves.
By listening to your body and making informed dietary choices, you can take control of your well-being and feel your best every day.