Collagen is one of the most important proteins in your body. It makes up roughly 30% of all the protein you have, playing a vital role in keeping your skin smooth, your joints strong, your hair and nails healthy, and your digestion running smoothly. It’s basically the structural glue that holds everything together.
But as you age, your body starts to produce less of it. And when that happens, your body begins to show it in unexpected ways. If you’ve noticed changes in your skin, joints, or even digestion, low collagen might be to blame.
1. Fine Lines and Wrinkles Are More Noticeable
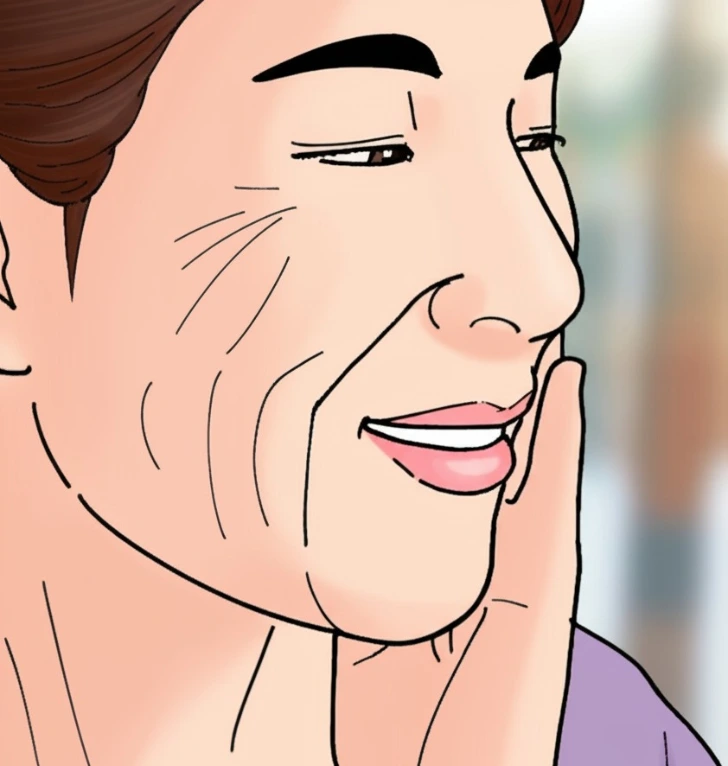

One of the earliest signs of collagen loss is the appearance of fine lines and wrinkles. Collagen helps your skin stay firm, elastic, and smooth. As collagen production slows down, skin starts to sag and crease. You might notice lines around your eyes, mouth, or forehead.
This change is a natural part of aging, but it can also be worsened by lifestyle factors like smoking, poor diet, or sun exposure. If your skin is losing its bounce and you’re seeing more wrinkles than usual, your collagen levels might be slipping.
Video:
8 Signs & Symptoms of A Collagen Deficiency?
2. Sagging Skin and Bumpy Texture (a.k.a. Strawberry Skin)
Have you noticed your cheeks or jawline starting to sag? That may be another signal your body isn’t producing enough collagen. When collagen levels dip, your skin loses its firmness and structure, which causes areas like the neck, jaw, and under-eyes to look looser or less lifted.
Some people also develop what’s commonly called “strawberry skin,” a rough, bumpy texture often caused by clogged pores or keratosis pilaris. Collagen plays a role in keeping skin smooth and elastic, so maintaining healthy levels can help improve both sagging and texture issues.
3. Your Skin Looks Dry or Dull
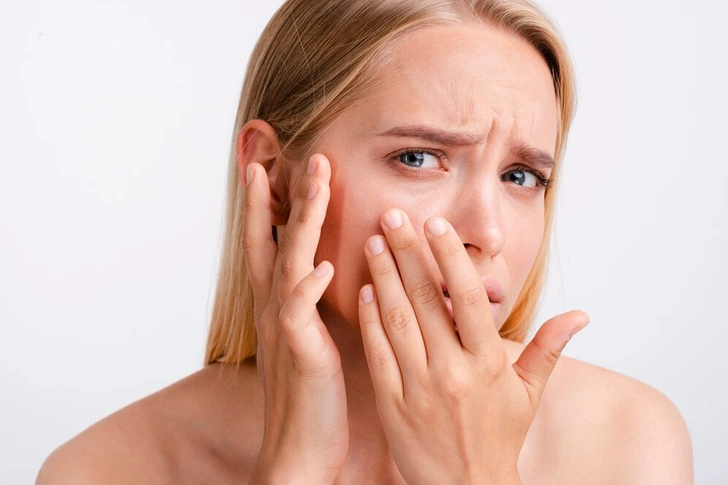

If your skin has lost its glow and feels dry or rough, collagen could be the missing link. Collagen helps your skin retain moisture and stay hydrated. Without enough of it, the outer layer of your skin can start to look dull, patchy, and lifeless.
A radiant complexion depends not only on hydration from the outside but also on internal protein support. By improving your body’s collagen production, you can help your skin regain its softness and natural shine.
4. Cuts and Bruises Heal Slowly
Slower healing after injuries is another red flag. Collagen is a key part of tissue repair, which means it’s responsible for helping wounds, cuts, and bruises heal efficiently. When collagen levels are low, healing takes longer — and scars may become more pronounced.
If you’ve noticed that your skin isn’t bouncing back as fast as it used to, or bruises are lingering longer than normal, it may be a sign your collagen production needs a boost.
5. Your Hair and Nails Are Weaker
Hair thinning and brittle nails are two often overlooked signs of collagen deficiency. Collagen provides strength to the hair shaft and the nail bed. When it’s lacking, you might experience increased hair shedding, dullness, or nails that peel and break easily.
If your hair seems to lack volume or your nails chip even with gentle use, it could be your body’s way of signaling a protein imbalance — specifically collagen.
Video:
Your Body Is Begging for Collagen
6. You Experience Joint Stiffness or Discomfort
Joint pain and stiffness aren’t just symptoms of aging — they can be directly linked to lower collagen levels. Collagen is a core component of cartilage, the cushiony tissue that keeps your joints moving smoothly.
As collagen breaks down, that cushion wears thinner, leading to discomfort and inflammation. If your knees creak, your hips ache, or you’re waking up stiff, increasing your collagen intake may help restore flexibility and reduce pain.
7. You’re Struggling with Digestive Issues

Not many people realize this, but collagen also plays a big role in gut health. It lines your digestive tract and helps maintain the integrity of your intestinal walls. If collagen levels dip, it can contribute to problems like leaky gut syndrome, where harmful substances leak through your intestinal lining and cause inflammation.
This can lead to symptoms like bloating, food sensitivities, or nutrient malabsorption. By supporting your collagen production, you can strengthen your gut lining and improve digestion.
What Causes Collagen to Break Down Faster
While aging is the primary factor in collagen loss, certain lifestyle habits can speed up the decline dramatically. Too much sun exposure, especially without SPF protection, damages collagen fibers over time. A diet high in refined sugar can cause a process called glycation, where sugars bind to collagen and make it rigid and fragile.
Chronic stress is another major culprit. High cortisol levels from prolonged stress can reduce collagen production and trigger inflammation. Add poor sleep and smoking to the mix, and your body’s natural collagen levels may drop faster than expected.
How to Support Your Body’s Collagen Production Naturally
Fortunately, there are several effective ways to boost your collagen levels without extreme interventions.
Start with your diet. Eating foods rich in protein, vitamins, and antioxidants can work wonders. Bone broth, chicken skin, egg whites, and fish all contain collagen. Fruits like oranges, strawberries, and kiwi are loaded with vitamin C, a nutrient essential for collagen synthesis.
Leafy greens and colorful vegetables provide powerful antioxidants that protect existing collagen from damage. Hydration is equally important — your skin needs water to stay supple and elastic.
Protect your skin from the sun with daily sunscreen. Even on cloudy days or indoors near windows, UV rays can damage your skin’s collagen network.
Get enough quality sleep each night. While you rest, your body repairs damaged cells and builds new collagen fibers. Aim for at least 7 to 9 hours of uninterrupted sleep.
Practice stress management through yoga, meditation, deep breathing, or spending time in nature. Reducing cortisol levels allows your body to focus on healing and rebuilding.
You may also want to consider collagen supplements. Hydrolyzed collagen peptides are easily absorbed by the body and have been shown in studies to improve skin hydration, elasticity, and even joint health.
Final Thoughts
Your body is always trying to communicate with you — and when collagen is low, it doesn’t stay quiet for long. From your skin to your joints to your gut, signs of collagen loss can show up in subtle but meaningful ways.
By paying attention to these early warning signs and adopting lifestyle habits that support collagen production, you can improve your overall health and well-being. Healthy collagen levels mean stronger skin, more flexible joints, better digestion, and a more youthful appearance.
Listen to your body. Support it with the right nutrients, rest, and care — and you’ll be amazed at how resilient it can be.